由于集群有流量的增長,以及開放新的服務出去,所以首先看了一下線程使用情況,未發現問題。
$JAVA_HOME/bin/jstack -l PID > jstack.out
grep -A 2 -B 5 -i "com.xxxxxx.xxxx" ./jstack.out 使用jstat查看GC情況發現PermGen將滿,并且頻繁觸發FGC,雖然能夠回收無效的類,但產生類的速度比FGC的效率還快,直接導致CPU使用率飆升。
ps -ef | grep java
$JAVA_HOME/bin/jstat -gcutil PID 1000 100
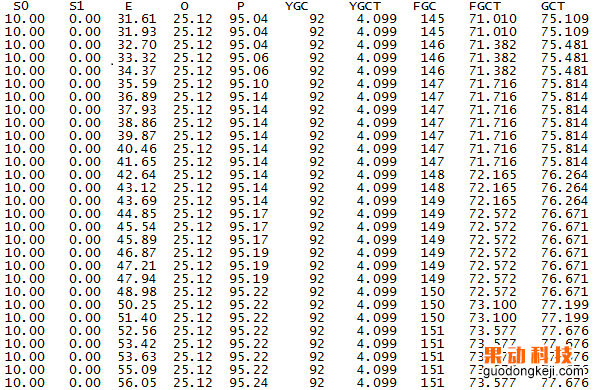
圖1 PermGen區升到95%引發頻繁FGC
遇到線上FGC問題常用的工具是用jmap & eclipse MAT來分析JVM內存使用情況了。網上資料很多,這里不在贅述,需要注意的一點是jmap是會觸發"stop the world"的,所以好是拉出來,然后做dump操作。如果用eclipse MAT分析切記提前把eclipse大能使用的內存調整下,否則分析上G的dump文件會掛掉。
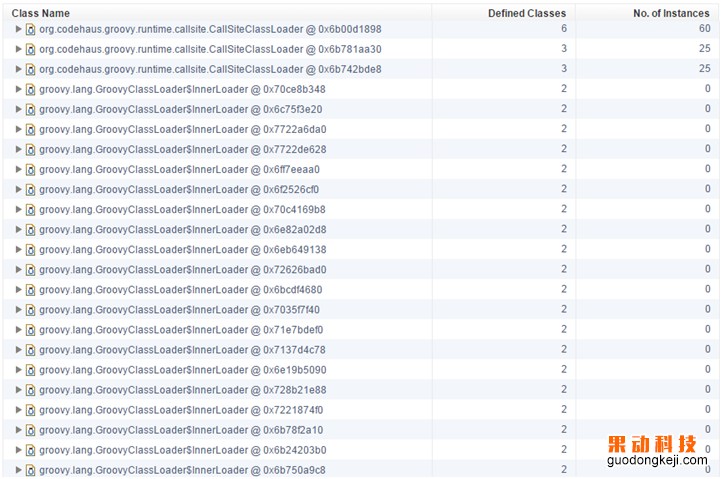
圖2 Dump中的類加載器情況
由于是PermGen區的泄漏,通過分析發現類加載部分有大量的GroovyClassLoader,這時想到有使用兩個服務,內部實現是使用Groovy配置的方式(這里我用Groovy封裝了一個服務提供的微框架)。但這兩個服務其實使用的并不頻繁,所以導致切換后的現象不是雪崩式的集群掛掉,而是慢慢的,逐步有機器load飆高告警。
定位到問題,事情就好辦了,首先看一下處理Groovy加載執行的代碼;然后為生成的類加一層對象緩存;由于腳本中用到了Binding上下文對象,為了線程安全性,調整執行時的方式。后問題得到解決。
Object scriptObject = null;
try {
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.setVariable("context", this.context);
binding.setVariable("clientInfo", clientInfo);
binding.setVariable("params", params);
binding.setVariable("data", data);
GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell(binding);
scriptObject = (Object) shell.evaluate(script);
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("groovy script eval error. script: " + script, t);
}
return scriptObject; private Map<String, Object> scriptCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
...
Object scriptObject = null;
try {
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.setVariable("context", this.context);
binding.setVariable("clientInfo", clientInfo);
binding.setVariable("params", params);
binding.setVariable("data", data);
Script shell = null;
if (isCached(cacheKey)) {
shell = (Script) getCaches().get(cacheKey);
} else {
shell = new GroovyShell().parse(script);
}
shell.setBinding(binding);
scriptObject = (Object) shell.run();
// clear
binding.getVariables().clear();
binding = null;
// Cache
if (!isCached(cacheKey)) {
shell.setBinding(null);
getCaches().put(cacheKey, shell);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("groovy script eval error. script: " + script, t);
}
return scriptObject; private Map<String, Object> scriptCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
...
Object scriptObject = null;
try {
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.setVariable("context", this.context);
binding.setVariable("clientInfo", clientInfo);
binding.setVariable("params", params);
binding.setVariable("data", data);
Script shell = null;
if (isCached(cacheKey)) {
shell = (Script) getCaches().get(cacheKey);
} else {
shell = cache(cacheKey, script);
}
scriptObject = (Object) InvokerHelper.createScript(shell.getClass(), binding).run();
// Cache
if (!isCached(cacheKey)) {
getCaches().put(cacheKey, shell);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("groovy script eval error. script: " + script, t);
}
return scriptObject; 這次碰到的問題還是很具有典型性的,其中的思路和用到的工具可以閱讀這兩本JVM相關的書籍獲取:《深入理解Java虛擬機》和《Java性能優化權威指南》。
本站文章版權歸原作者及原出處所有 。內容為作者個人觀點, 并不代表本站贊同其觀點和對其真實性負責,本站只提供參考并不構成任何投資及應用建議。本站是一個個人學習交流的平臺,網站上部分文章為轉載,并不用于任何商業目的,我們已經盡可能的對作者和來源進行了通告,但是能力有限或疏忽,造成漏登,請及時聯系我們,我們將根據著作權人的要求,立即更正或者刪除有關內容。本站擁有對此聲明的最終解釋權。
